OLED display has high contrast, bright color, and is self-luminous, which is more transparent than LCD display. Meanwhile, it can be folded, making it the first choice for flagship smartphones. Have you noticed that if you look at an OLED screen for a long time, your eyes will be uncomfortable, and you will feel dizzy and irritable because OLED screens flicker? Today we are going to discuss why OLED screens flicker.
1. The reasons why OLED flickers
OLED screens are not always on but are on and off repeatedly to control the brightness so that flickering happens. However, due to its high frequency, human eyes generally cannot distinguish the flickering.
2. OLED dimming mode: PWM dimming (pulse wave modulation dimming)
The brightness of OLED screens is controlled by constantly turning on and off of the screen. When the frequency is high enough, it can’t be distinguished by the naked eye (so-called PWM dimming).
In PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) dimming, the power is not changed, but the screen flickers alternately in a very short time with a specific frequency of “on → off → on → off”. By adjusting the time ratio of “on” and “off”, the screen brightness level can be adjusted from 0% to 100%.
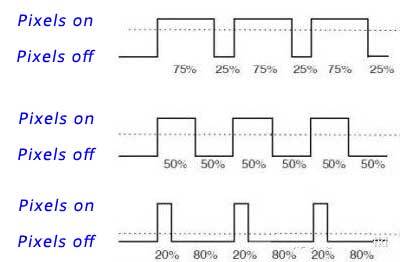
In this process, the screen does not really become dim or bright. For example, suppose the duration of the “off” status is prolonged (the duration of the “on” status is reduced). In that case, people will have the illusion that the screen has become dimmer, which is called the visual persistence phenomenon. If the brightness of the screen is 100%, it means the screen is on for the whole cycle. If the brightness is 80%, it means the screen is turned on 80% of the time and off 20% of the time in a cycle. If the brightness is 50%, the on and off time becomes 50% and 50% in a cycle. Under low brightness, our naked eyes will obviously discover that the screen is turned on and off if the screen is off for too long. Many people mistakenly think that the flickering frequency of the screen becomes lower, but the screen is off for too long, resulting in too obvious a black field interval.

2.1 Advantages of PWM dimming
PWM dimming has many advantages, such as simple structure, no color deviation, power saving, and low heat generation. However, flickering exists.
2.2 Disadvantages of PWM dimming
People mostly criticize PWM dimming for its screen flickering. In PWM dimming, if the screen flickers 500 times per second, the frequency of PWM flickering is 500Hz. Generally, once the frequency exceeds 80Hz, it is difficult to detect it with the naked eye, and a professional camera is needed to shoot at the screen to discover the flickering. At present, the flickering frequency of the PWM dimming of OLED screens on many mobile phones is about 215Hz-250Hz.
Human eyes can’t detect it, but visual cells can. Cells can sense subtle changes in the brightness of light, which drives muscle adjustment. PWM dimming frequently adjusts the brightness of the screen, which will stimulate nerves and cause visual fatigue. The lower the brightness of OLED screens, the smaller the frequency of the flickering, and the more significant the impact on human eyes. Therefore, many people suggest that we should not use smartphones without lighting at night, especially those with OLED screens.
But the problem is that in PMW dimming mode, the brightness of the pixel light source will be maximum as long as it lights up, which is more likely to lead to visual fatigue no matter how high the brightness is. Everyone has a different sensitivity to flickering. Therefore, there has been no clear conclusion in electrical and medical circles about the specific safe Hz value of PWM dimming. However, there is still a chance that brain and retinal tissue can still detect and respond to the flickering, which is manifested by eye fatigue and migraine headache.
You will suddenly feel eye swelling and headache when playing games or reading novels on your mobile phone for a long time. On the one hand, your body is tired; on the other hand, this may be caused by PWM dimming. For example, I have two mobile phones at hand. One is the Oneplus 7pro, and the other is the Oneplus 8T. The maximum brightness activated manually of Oneplus 7pro is 800nit, while Oneplus 8T is 1100nit. If I watched the screen of Oneplus 8T for more than 1 hour, my eyes would feel tired.
3. Why does OLED flicker but not LCD screens?
DC dimming (Direct Current dimming) is a way to adjust the brightness of the screen. Nowadays, portable devices such as smartphones all have light sensors, which can automatically adjust the brightness of the screen by sensing the brightness of the environment. DC dimming changes the brightness of the screen by increasing or decreasing the power of the circuit of the screen panel. Since power is equal to voltage * current, the brightness of the screen can be changed only by changing the voltage or current.
After reducing the flickering of the screen, users’ eyes will be less uncomfortable and less harmed if they stare at the screen for a long time. This is the advantage.
However, the disadvantage is that DC dimming will influence the uniformity and brightness accuracy of the screen displays, especially the color difference of the screen under low brightness.
LCD screens support DC dimming. Thus they do not flicker. PWM dimming is applied to OLED screens, which adjust the brightness of the screen by turning the screen on and off alternatively under a specific frequency, thus resulting in severe flickering.
4. Why is PWM dimming applied to OLED screens?
When DC dimming is started on an OLED screen, all kinds of deviations will always appear on the screen. Moreover, there will be an uneven rolling shutter effect under low voltage. Therefore, we cannot adjust the brightness of OLED screens by using DC dimming.
When the OLED screen is on for a long time, the decay rate of RGB sub-pixels in each pixel is different. In this case, there will be screen burn-in, even more severe.
Therefore, PWM dimming has become the preferred dimming scheme for OLED screens. This way can well control the burn-in of screens.
5. What is the principle of DC function in OLED smartphones?
In fact, the principle is to use algorithms or hardware to speed up the “on and off frequency” of OLED screens to reduce flickering. PWM dimming is still used, but the screen is more like it is DC-dimmed.

6. How to avoid OLED flickering:
6.1 We can use the “Flickering Protection” APP to alleviate the flickering of OLED screens at low brightness.
6.2. When running the APP, it will prompt us to enable the permission of barrier-free service. Next, you can modify the pixel filtering level and basic physical brightness through the pop-up window. Clicking the “Start Service” button in the upper right corner of the window to make it effective, as shown in the image:
6.3. Eyes are protected by reducing the screen’s brightness by turning off some pixels and adding a transparent black mask layer.
6.4. When the APP starts, you will feel the screen dimmer (there is no flickering problem in this darkness). Therefore, it is most suitable for night or an environment with poor lighting. It can replace the automatic reduction of brightness of the screen (when there is flickering), thus solving the problem!
7. The final solution for OLED flickering: high-frequency PWM dimming
At present, BOE, a domestic brand, has taken the lead in realizing the 1920Hz high-frequency PWM dimming scheme on OLED screens and applied it on the newly released smartphone, Redmi K50 e-sports version.
This high-frequency dimming has a screen flickering frequency far exceeding traditional low-frequency dimming. When using high-frequency PWM dimming, the time interval between the screen on and off is very small, which is almost imperceptible to the naked human eyes. Therefore, our eyes will not be tired. Moreover, PWM dimming has another advantage: there is no color difference on the screen under low brightness, unlike DC dimming. Presumably, high-frequency PWM dimming will replace low-frequency PWM as one of the benchmark indicators for future certification of top screens.
OLED techniques in the future will accelerate the speed of flickering so that neither the naked eye nor the machine can detect the flickering of the screen. At that time, the OLED technique could be called a mature technique. At present, screen manufacturers such as Samsung and LG still have a long way to go.